As we grow older, the importance of health insurance cannot be overstated. Having adequate health coverage ensures that we can access quality medical care when we need it most, without worrying about the financial burden that comes with it. For many, this means enrolling in Medicare, a federal health insurance program for individuals who are 65 and older or those who have certain disabilities. However, those who already have private health insurance may wonder if they need to enroll in Medicare as well.
The answer to this question is not a straightforward one. While private health insurance can provide comprehensive coverage, there are certain gaps that Medicare can fill. In this article, we will explore the differences between private health insurance and Medicare, the benefits of both, and help you make an informed decision on whether you need Medicare if you already have private health insurance.
If you have private health insurance, you may wonder if you need Medicare. While it’s not mandatory, enrolling in Medicare can provide additional coverage and help lower out-of-pocket costs. Medicare can also be beneficial if you lose your private insurance or if it doesn’t cover certain medical expenses. Ultimately, the decision to enroll in Medicare depends on your individual healthcare needs and financial situation.
Do I Need Medicare if I Have Private Health Insurance?
If you have private health insurance, you may be wondering whether you need to sign up for Medicare. The answer to this question depends on a variety of factors, including the type of private health insurance you have and your individual healthcare needs. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of having private health insurance and Medicare, as well as provide guidance on how to determine whether you need both.
What is Private Health Insurance?
Private health insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides coverage for medical expenses. This type of insurance is typically purchased by individuals or provided by employers as a benefit to employees. Private health insurance policies can vary in terms of coverage, deductibles, co-pays, and premiums. The coverage provided by private health insurance can include hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, and other medical services.
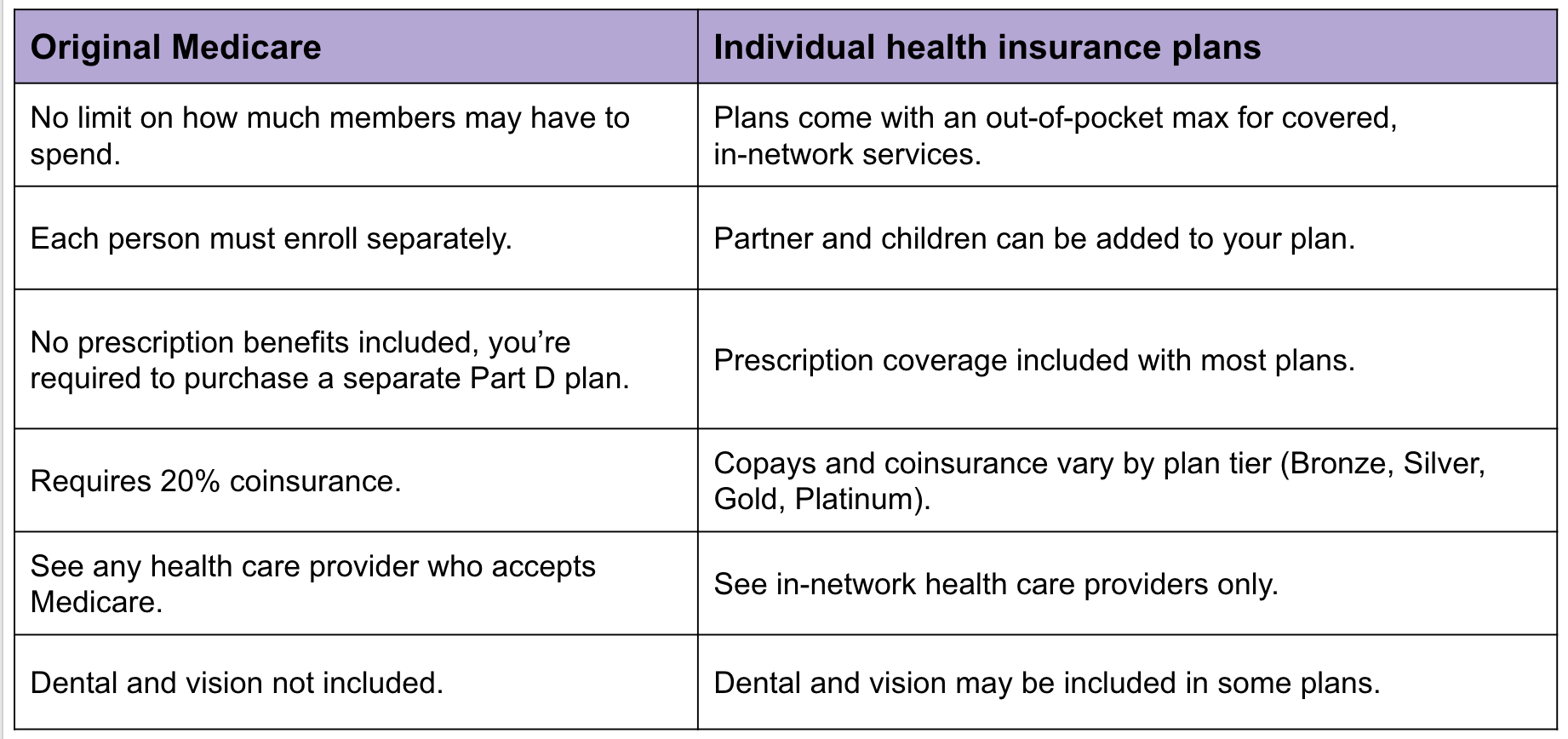
There are several advantages to having private health insurance. One of the main benefits is that it can provide more extensive coverage than Medicare. Private health insurance policies can cover services that Medicare does not, such as dental care, vision care, and alternative therapies. Additionally, private health insurance policies can be customized to meet individual healthcare needs.
However, there are also some disadvantages to private health insurance. Private health insurance policies can be expensive and may require high deductibles or co-pays. Additionally, some private health insurance policies may have restrictions on where you can receive medical care, which can limit your options for healthcare providers.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals who are 65 years old or older, as well as individuals with certain disabilities. Medicare is divided into four parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. Part A covers hospital stays, Part B covers doctor visits and other medical services, Part C (also known as Medicare Advantage) is a combination of Parts A and B, and Part D covers prescription drugs.
One of the main advantages of Medicare is that it is typically less expensive than private health insurance. Additionally, Medicare provides coverage for a wide range of medical services and has a large network of healthcare providers. Medicare can also provide coverage for individuals with pre-existing conditions, which may be excluded from private health insurance policies.
However, there are also some disadvantages to Medicare. Medicare does not cover all medical services, and there may be gaps in coverage that require individuals to pay out-of-pocket for certain medical expenses. Additionally, some healthcare providers may not accept Medicare, which can limit your options for medical care.
Do I Need Both?
Whether you need both private health insurance and Medicare depends on your individual healthcare needs and the type of insurance policies you have. If you have comprehensive private health insurance that covers all of your healthcare needs, you may not need Medicare. However, if your private health insurance has limitations or gaps in coverage, you may want to consider signing up for Medicare to fill those gaps.
Additionally, if you are 65 years old or older, you may be required to sign up for Medicare. If you do not sign up for Medicare when you are first eligible, you may face penalties and higher premiums when you do decide to sign up.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance and Medicare
There are several benefits to having both private health insurance and Medicare. Having both types of insurance can provide comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical services. Additionally, having both types of insurance can give you more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and receiving medical care.
Private Health Insurance Vs. Medicare
When comparing private health insurance and Medicare, it is important to consider the cost, coverage, and limitations of each. Private health insurance can provide more extensive coverage than Medicare, but it can also be more expensive. Medicare is typically less expensive than private health insurance, but it may have gaps in coverage that require individuals to pay out-of-pocket for certain medical expenses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, whether you need both private health insurance and Medicare depends on your individual healthcare needs and the type of insurance policies you have. If you have comprehensive private health insurance that covers all of your healthcare needs, you may not need Medicare. However, if your private health insurance has limitations or gaps in coverage, you may want to consider signing up for Medicare to fill those gaps. Ultimately, the decision of whether to have both private health insurance and Medicare is a personal one that should be based on your individual healthcare needs and financial situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I Need Medicare if I Have Private Health Insurance?
Medicare is a government-funded health insurance program for people aged 65 and above or those who have certain disabilities. Private health insurance, on the other hand, is insurance provided by private companies. If you have private health insurance, you may not need to enroll in Medicare, but it depends on the type of private insurance you have and your personal situation.
If your private insurance is a Medicare Advantage plan, you do not need to enroll in Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans are offered by private insurance companies that contract with Medicare. These plans provide the same benefits as original Medicare, and sometimes additional benefits like dental, vision, and hearing care. However, if you have a private insurance plan that does not include Medicare benefits, you may need to enroll in Medicare to avoid paying penalties.
Can I Use Medicare and Private Insurance Together?
Yes, you can use Medicare and private insurance together. This is called coordination of benefits. If you have both Medicare and private insurance, one of the plans will be the primary payer, and the other will be the secondary payer. The primary payer will pay its share of the bill first, and the secondary payer will pay the remaining balance, up to the limits of its policy.
If you have Medicare and a retiree health plan from a former employer, the retiree plan is usually the primary payer. If you have Medicare and a current employer health plan, the employer plan is usually the primary payer if you work for an employer with 20 or more employees. If you work for an employer with fewer than 20 employees, Medicare is usually the primary payer.
Will My Private Health Insurance Cover Everything That Medicare Does?
Private health insurance plans vary widely in terms of what they cover, so it’s important to carefully review your plan’s coverage before deciding whether you need Medicare. Medicare covers a wide range of medical services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. Private health insurance plans may offer similar coverage, but they may also have restrictions on what they cover and how much they pay.
If you have a Medicare Advantage plan, your plan must provide the same benefits as original Medicare, but it may also offer additional benefits. If you have a private insurance plan, you should review the plan’s summary of benefits to determine what is covered and what is not. You should also check whether your plan has any deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance that you will be responsible for paying.
What Happens If I Don’t Enroll in Medicare When I’m Eligible?
If you are eligible for Medicare and do not enroll during your initial enrollment period, you may have to pay a penalty when you do enroll. The penalty is typically 10% of the Medicare Part B premium for every year that you were eligible for Medicare but did not enroll. The penalty can be significant, so it’s important to enroll in Medicare when you are first eligible.
There are some exceptions to the penalty, such as if you have creditable coverage through an employer plan, but you should still enroll in Medicare when you are first eligible to avoid any potential penalties.
Can I Change My Mind About Enrolling in Medicare?
Yes, you can change your mind about enrolling in Medicare. If you initially opted out of Medicare but later decide you want to enroll, you can enroll during the general enrollment period, which runs from January 1 to March 31 each year. Your coverage will begin on July 1 of that year.
If you enrolled in Medicare but want to switch to a Medicare Advantage plan, you can do so during the annual open enrollment period, which runs from October 15 to December 7 each year. You can also switch back to original Medicare during this period.
Do I Need Medicare If I Have Private Insurance? 
In conclusion, choosing between Medicare and private health insurance can be a confusing decision for many people. While private health insurance offers more flexibility and personalized coverage, Medicare provides comprehensive coverage at a lower cost for those who are eligible. Ultimately, the decision to enroll in Medicare should be based on individual circumstances such as age, health status, and financial situation.
Regardless of whether you choose Medicare or private health insurance, it is important to have adequate healthcare coverage. Medical expenses can quickly add up, and having insurance can provide peace of mind and financial protection. As a professional writer, my advice is to carefully consider your options and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your unique situation.
Meet Rakibul Hasan, the visionary leader and founder of Freeinsurancetips. With over a decade of experience in the insurance sector, Rakibul is dedicated to empowering individuals to make well-informed decisions. Guided by his passion, he has assembled a team of seasoned insurance professionals committed to simplifying the intricate world of insurance for you.
- Latest Posts by Rakibul Hasan
-
Can I Keep Medicaid If My Job Offers Insurance?
- -
Does Smile Direct Club Take Medicaid Insurance?
- -
Does Life Insurance Payout Affect Medicaid?
- All Posts
